|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
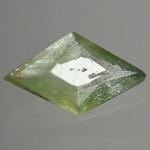
Ludlamite
|
|
| | |
| Discovered in 1877; IMA status: Valid (pre-IMA; Grandfathered) | ||
|
| ||
|
Chemistry |
|
|
| |
|
(Fe2+,Mg,Mn2+)3(PO4)2 • 4H2O | |
|
|
Hydrated Iron Magnesium Manganese Phosphate |
|
Molecular Weight: |
400.88 gm |
|
Composition: |
Magnesium |
5.46 % |
Mg |
9.05 % |
MgO |
|
|
Manganese |
4.11 % |
Mn |
5.31 % |
MnO |
|
|
Iron |
25.08 % |
Fe |
32.26 % |
FeO |
|
|
Phosphorus |
15.45 % |
P |
35.41 % |
P2O5 |
|
|
Hydrogen |
2.01 % |
H |
17.98 % |
H2O |
|
|
Oxygen |
47.89 % |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
100.00 % |
|
100.00 % |
= TOTAL OXIDE |
|
|
|
||||
|
Classification |
|
|
| |
|
Phosphates | |
|
7/C.10-10 | |
|
|
8 : PHOSPHATES, ARSENATES, VANADATES
|
|
Related to: |
Isostructural with Metaswitzerite, Sterlinghillite, Switzerite. |
|
Varieties: |
None |
|
Synonyms: |
Lehnerit (of Müllbauer) |
|
|
|
|
Crystal Data |
|
|
|
|
|
As crystals, usually tabular, to 9 cm, may be in parallel groups; granular, massive. |
|
|
None |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Properties |
|
|
|
|
|
Perfect on [001], Indistinct on [100] |
|
|
Conchoidal |
|
|
Slightly brittle |
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
3.12 - 3.19 (g/cm3) |
|
|
None |
|
|
Not Radioacitve |
|
|
Other: |
Diamagnetic. Soluble in acids. |
|
|
|
|
Optical Properties |
|
|
|
|
|
Apple-Green to bright Green; nearly Colorless in transmitted light |
|
|
Transparent to Translucent |
|
|
Vitreous, Pearly on cleavage [001] |
|
|
1.650 - 1.697 Biaxial ( + ) |
|
|
0.038 - 0.044 |
|
|
Perceptible; r > v |
|
|
None |
|
|
|
|
|
Occurances |
|
|
|
|
|
Geological Setting: |
In complex granite pegmatites, a common hydrothermal alteration product of earlier phosphates, formed under reducing conditions. |
|
Common Associations: |
Apatite, Phosphoferrite, Triphylite, Triplite, Triploidite (Hagendorf, Germany); Fairfieldite, Siderite, Vivianite, Whitlockite (Palermo #1 mine, New Hampshire, USA). |
|
Common Impurities: |
n/a |
|
Type Locality: |
Wheal Jane (Falmouth Consolidated; Wheal Whidden; Wheal Nangiles; Wheal Tremayne), Baldhu, Camborne - Redruth - St Day District, Cornwall, England, UK |
|
Year Discovered: |
1877 |
|
View mineral photos: | |
|
Unusual Gem Categories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Magnetic Gems (diamagnetic) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
More Information |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
Ludlamite is unusual in that it is a diamagnetic mineral. Diamagnetism is a form of magnetism where certain minerals are repelled by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal induced magnetic fields in the direction opposite to that of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, some minerals, such as Xenotime, are paramagnetic. Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism where certain minerals are attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. Ludlamite was named in 1877 by English geologist Nevil Story Maskelyne (1823–1911) and English chemist Frederick Field (1826-1885) in honor of their friend, English mineral collector Henry Ludlam (1824-1880), London, England. Ludlamite was first described in 1877 for an occurrence at the Wheal Jane Mine, St. Day District, Cornwall, England. There are only a few
locations for facetable crystals. These include the
Wheal Jane Mine, Truro, Cornwall, England
(the Type Locality); Morococala and Huanuni, Oruro,
Bolivia; Rapid Creek,
Yukon Territory, Canada; Hagendorf, Bavaria, Germany; San Antonio mine, Santa
Eulalia district, Chihuahua, Mexico; the Blackbird mine,
Lemhi County, Idaho, USA;
the Palermo #1 mine, North Groton, Grafton County, New Hampshire; and Custer County, South Dakota, USA. |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||